–GlobalData ranks Huawei’s 5G RAN as the market leader
LONDON, Jan. 15, 2021 /PRNewswire/ — Innovation is the basis for the long-term development and evolution of the mobile communications industry. In the 5G era, mobile communications networks carry more missions and meet diversified requirements for network capabilities, operation efficiency improvement, and business success. 5G continuous innovation becomes particularly important.
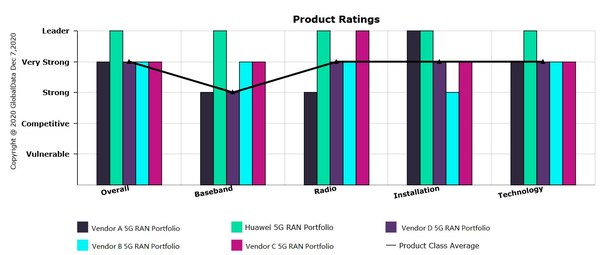
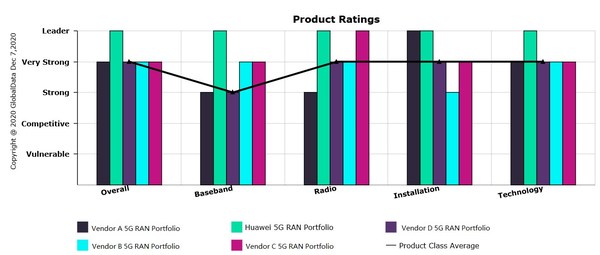
According to the GlobalData’s recent competitiveness evaluation report on mainstream vendors, Huawei 5G RAN ranks No.1 in all dimensions, demonstrating the competitive advantages of products and solutions. In addition, Huawei announced latest 5G network development concept and launched innovative products and solutions.
Huawei 5G RAN Leadership
GlobalData, a leading market data and analytics company, has rated Huawei’s 5G RAN portfolio to be a Leader in the market. In competitive analyses of five major RAN vendors, GlobalData evaluated 5G base station portfolios according to four key areas important to mobile operators: baseband unit (BBU) capacity, radio unit portfolio breadth, ease of installation and technological evolution. GlobalData found Huawei to be a Leader in all four categories and a Leader overall among its peers(the mainstream vendors).
Huawei reports the highest BBU cell capacity – for both sub-6 GHz and millimeter-wave spectrum – of any major RAN vendor. It also offers more radio units and more Massive MIMO options than other vendors and supports a wide array of 5G spectrum bands. To make deployment easier, Huawei has multiple novel solutions, including its Super BladeSite and Bracelet Kit offerings. And to help operators evolve their networks technologically, Huawei has been proactive in commercializing spectrum-sharing capabilities such as its CloudAIR solution, which allows various access technologies (2G/3G/4G/5G) to use the same spectrum, and its SuperBAND solution, which allows these technologies to share network resource blocks.
This portfolio is well-suited to meet the diverse needs of the world’s mobile operators, and Huawei continues to expand its portfolio to address current and future challenges that operators face on the journey to achieving the 1 + N network.
The 1 + N Network: An Intelligent, Versatile Network
The 5G era holds enormous potential for mobile operators to grow profitability by expanding into new services and tapping new revenue sources. But the network and business transformation required to capture these opportunities introduces new levels of complexity in network deployment and management and service delivery. There are ways for operators to tackle this complexity with networks that are as diverse and sophisticated as the new world of services the market demands.
To help operators capture new opportunities despite the challenges of network complexity, Huawei employs what it calls a "1 + N" concept, vowing to "build one foundational network for high-bandwidth ubiquitous connectivity – ‘N’ capabilities deployed on demand." 1 + N is the concept of a single, unified network addressing an expandable variety of network needs and services. This concept – maximizing the revenue generated by a single infrastructure investment – is key to how 5G can help operators become more profitable.
New innovations added to Huawei’s 5G RAN portfolio help operators achieve the 1 + N network, including the Blade Pro solution, the Adaptive High Resolution algorithm, the Mobile Broadband Automation Engine and more.
Operators’ Network Challenges
As operators evolve for the 5G era, they will increase the capacity of their public networks using a range of new spectrum bands. However, making use of these spectrum bands while continuing to support legacy networks poses many challenges, including:
- Fragmented spectrum assets can breed inefficiency
- Diversified channels and sectors can increase network management complexity
- Differences in frequency-band life cycles can impact operators’ ability to use certain radio access technologies in certain spectra
- Limited Antenna Space brings deployment challenges
Huawei has developed new offerings within its RAN portfolio to tackle all of these challenges and more.
The Blade Pro Solution
To help simplify networks and address these challenges, Huawei has long committed to a Single RAN strategy of using a single network to deliver multiple technologies. Its newest RAN offerings, part of Huawei’s 1 + N vision, continue to help in these areas.
Huawei’s Blade Pro offering is designed to help simplify deployment and ease installation and network management, reducing operators’ costs. The Blade Pro Ultra-Wideband Remote Radio Unit (RRU) is a pole-mountable 4G/5G RU that supports three low or medium Frequency-Division Duplex (FDD) bands simultaneously: it will support 700, 800 and 900 MHz as well as 1.8, 2.1 and 2.6 GHz, allowing operators to build a single foundational network for ubiquitous connectivity using mid-band spectrum.
By supporting three frequency bands in a single 25-kilogram unit, the Blade Pro eliminates the need for two boxes, reducing the load on poles, easing the burden on installers and making deployment faster, smoother and less expensive.
The Blade Pro also helps operators address the three challenges cited above. Tri-band support helps reduce the complexity of fragmented spectrum by pulling multiple bands into a single network management point. A software-defined antenna allows operators to change the number of receivers or sectors via software rather than hardware, overcoming the challenges of channel and sector diversity in operator networks. In addition, where operators need to make changes based on which technologies – LTE or 5G NR – are delivered over which spectrum bands, a software-defined antenna helps to make those changes easier as well.
The BladeAAU Pro Solution
In addition to the Blade Pro, Huawei has also introduced the BladeAAU Pro solution, a Massive MIMO product with 32T32R and 64T64R antenna array options that supports sub-3 GHz bands. Huawei designed the BladeAAU Pro to ensure high-quality experiences for 5G users while simplifying deployment for operators, minimizing deployment costs and addressing the challenges of antenna space limitations.
5G Software Innovation: Adaptive High Resolution (AHR) Algorithm
Huawei further enhances the network capabilities with another offering: the Adaptive High Resolution (AHR) algorithm, which significantly improves the capacity and user experience of Massive MIMO cells in scenarios with high user density and a strong potential for signal interference.
However, the above new solutions are not the only way Huawei’s portfolio is evolving to fulfill the vision of 1 + N networks.
1 + N O&M
One of the most significant challenges operators will face in adopting 1 + N networks is in performing the Operations and Maintenance (O&M) that can address complex, multi-functional networks while limiting the burdens of that complexity on operators’ human personnel. In order to achieve both ends, 1 + N networks must embrace new levels of automation.
To achieve this task, Huawei envisions what it calls the Autonomous Driving Network, drawing an analogy between self-driving automobiles and the intelligent networks of the future.
Huawei’s vision for Autonomous Driving Network includes five levels of automation:
- Tool assistance
- Partial autonomy
- Conditional autonomy
- High autonomy
- Full autonomy
Today Huawei’s solutions represent a level of autonomy approaching the third level, "conditional autonomy;" they are projected to gradually evolve over time to include all five levels by 2030. But Huawei’s Autonomous Driving Network is already addressing multiple O&M challenges in the 1 + N network.
O&M Challenges
Some specific hurdles for O&M operations in 1 + N networks include:
- Managing multiple radio access technologies (2G, 3G, 4G, 5G) simultaneously
- Effectively delivering new services tailored for business customers
- Balancing user experience quality with network energy consumption
- Optimizing network conditions such as latency, bandwidth, uplink and downlink
To address these challenges, Huawei’s Mobile Broadband Automation Engine (MAE) solution helps operators manage networks comprehensively and intelligently using artificial intelligence (AI).
Multi-RAT, Multi-Band
Most networks transition over time from one radio access technology (RAT) to the next, forcing operators to manage more than one network at the same time, such as 4G and 5G. This duality increases the complexity of the network and the costs associated with network maintenance. These multi-RAT networks are even more complex because they include multiple frequency bands within those RATs. In addition, government regulators in some countries limit the transmission power of base stations to the extent that operators are forced to allocate power to various frequency bands in ways that are inefficient and can limit coverage.
Huawei’s MAE helps make multi-band, multi-RAT networks more efficient by coordinating RATs under a unified management scope and automating optimization of the combined network. For example, MAE analyzes network traffic behavior using measurement reports from user equipment and automatically shifts traffic from one band to another based on the optimal performance and energy efficiency parameters. The solution also coordinates power allocation among multiple frequency bands, allowing operators to avoid inefficiency and coverage limitations due to regulatory power restrictions.
Even more complex than multi-RAT, multi-band networks are the diverse set of requirements stemming from advanced business services.
5G to Businesses
For operators to capture opportunities in offering new services to business clients beyond connectivity, their networks will need to support a variety of capabilities on a case-by-case basis. For example, automated and remotely-operated vehicles that are enabled by wireless networks require low latency to avoid error and collision. Video surveillance use cases, on the other hand, require high-bandwidth uplink connections. Meanwhile, equipment sensors on industrial or agriculture sites might not need high bandwidth or low latency but require high reliability and enough energy efficiency to preserve battery life.
Huawei’s "5GtoB" suite helps operators address the diversity of business needs in multiple ways – at the planning, deploying and management stages.
First, Huawei’s intelligent planning tools help operators anticipate not only network construction requirements but radio resource slicing considerations, using artificial intelligence analysis of network traffic models, user device types and other large data sets. The solution takes service-level agreements into the planning process in order to ensure networks will have the slicing capabilities to support service performance needs. It also translates network construction requirements, removing barriers in the process.
The 5GtoB suite also speeds and simplifies business service provisioning on demand by automatically establishing network characteristics such as cells, features and network resources, allowing operators to launch campus network services in hours rather than days. These automatic processes also allow operators to make changes quickly if needed, with less need for manual intervention. They also make O&M more proactive, using AI to not only monitor but predict performance changes from both the network and device side, forecasting network problems as much as 15 days in advance and presenting visualizations of network performance at the network, slice and enterprise-customer levels.
Finally, the 5GtoB suite optimizes the network in order to deliver a range of different service characteristics to each slice of the network – ensuring that low latency, high-bandwidth uplink and high-reliability connections are all supported according to their respective needs while coordinated by the 1 + N network to make the most efficient use of network resources. The intelligent network uses AI capabilities to maximize energy efficiency without sacrificing the required quality of experience for each service.
Conclusion
Huawei recognizes that networks and their operations will need to evolve in order to capture the wealth of diverse opportunities that lie ahead. They will need to evolve in terms of planning, provisioning, installation, management and optimization. The complexity of these combined tasks will require networks to adopt new levels of intelligence and automation. This transformation won’t happen overnight but will evolve in stages. And the early stages in that evolution are already happening today within Huawei’s RAN portfolio.