BEIJING, Jan. 5, 2022 /PRNewswire/ — A news report from China Daily on Guiyang.
Success of agricultural sector sees output and profits of Guizhou province rise substantially.
As a key edible fungus demonstration zone in Guizhou province, Baiyun district in Guiyang city is integrating the industry with modern technologies and boosting the high-quality development of the entire industrial chain through a series of initiatives, said local officials.
Edible fungus is one of Guizhou’s 12 major characteristic agricultural industries. In the past four years, the province’s edible fungus output has increased by 51.4 percent per year and its value has increased by 60.7 percent per year.
In 2020, the output of edible fungi in Guizhou reached 1.48 million metric tons, with an output value of 18.4 billion yuan ($2.89 billion).
The growth rate ranks first in the country, and the overall scale pushes it into the top 10 in the country.
As of the end of October, a total of 21 edible fungus bases have been built in Baiyun. Since 2016, 176.9 million fungus sticks have been planted, with an output of 86,700 tons and an output value of 1.02 billion yuan.
The edible fungus in Baiyun is equipped with a full chain tracking management model from the production, cultivation, processing and certification to testing phases.
Liao Yiren, manager of Intelligent Fungus Cloud, an online platform for the entire industry chain of edible fungi, said based on cutting-edge technologies such as big data, the internet of things and artificial intelligence, the platform focuses on areas of production, planting, processing, supply and marketing, certification and testing.
To date, the platform has established 31 data collection points, with 15 edible fungus companies, cooperatives, bases, and large households.
Guizhou Jukong Technology is one of the enterprises on the platform. It has established the first intelligent base for rare edible fungi in Baiyun, which not only improves the standardization and automation of edible fungi production, but also the utilization rate of agricultural resources as well as easing the shortage of land resources.
Zou Liqin, 49, a local villager in Asuo village working at the edible fungus base, said she is thankful for the job. "Working eight hours a day, I can earn 4,000 yuan a month. It takes me five minutes to ride an electric bike from home. It is very convenient to take care of my children."
To date, the base has employed more than 50 local farmers.
Guizhou Zhongke Yinong Technology is another edible fungus processing enterprise in this area.
"This is a freeze-dried morel mushroom. Based on the base pre-harvest period and pre-production data provided by the platform, combining with the actual situation of the edible fungus entering the processing plant to its storage, we reasonably arrange the processing time and processing quantity, and implement planned processing," said Zhang Ke, chairman of the company.
"We use the processing workshop module to provide standardized production parameters to ensure that downstream companies’ requirements for the production standards of primary processed products are met.
"At the same time, we have gradually formed our own standardized production system. The data and videos of the processing workshop make the processing steps more transparent and help with standardization," he added.
In order-based procurement and sales, the company can sign order-based production agreements with upstream and downstream companies through the system and implement order-based production and sales planning arrangements. The production end is only responsible for planting and processing, and the platform is responsible for sales.
In the Guizhou Mushroom Museum, visitors can understand all the information about the entire industrial chain process of the products from rod making, cultivation and processing to sales.
They can also use blockchain technology to ensure the safety and reliability of information and data, and help producers build trust in quality and safety assurance.
Covering a total construction area of nearly 2,000 square meters, the Guizhou Mushroom Museum includes functional areas of science, culture, creativity and research.
The museum introduces edible fungi-related knowledge and their development through graphic introductions, specimen displays and taste activities.
Fan Xuanxiang, deputy director of the education bureau of Baiyun, said the district will enhance edible fungus education and launch research activities to boost the local culture.
Last year is the first year of the implementation of the 14th Five-Year Plan period (2021-25) and a crucial year for comprehensively promoting rural revitalization.
Guiyang will strive to make new breakthroughs in rural revitalization and make positive contributions to the construction of a vibrant Guizhou. On Sept 26, Hu Zhongxiong, a member of the Standing Committee of the Guizhou Provincial Party Committee and Party secretary of Guiyang, presided over a special meeting on agricultural modernization in Guiyang. He said that it is necessary to stabilize the basic agricultural market.
Guiyang’s economic growth has increased by 284.3 percent in the past 10 years. In 2020, there are more than 5,000 big data companies in Guiyang and the added value of the digital economy exceeded 160 billion yuan, accounting for more than 38 percent of the region’s GDP.
"Big data has become an important engine for Guiyang’s high-quality development, allowing Guiyang to stand at the forefront of the world to showcase its beauty to all," said Ma Ningyu, deputy Party secretary and acting mayor of Guiyang.
"At present, Guiyang is promoting the deep integration of big data and rural revitalization," Ma said.
During the 14th Five-Year Plan period, Guiyang will promote the construction of optical fiber connections in administrative villages, optimize the extension of the 5G network of administrative villages to natural villages with more than 30 households and increase the scale and functions of radio and television cloud coverage.
Guiyang will build a national digital agriculture and rural innovation center and a digital agriculture application promotion base, develop smart agriculture, and promote the use of information technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain in agricultural planting, breeding, processing and logistics.
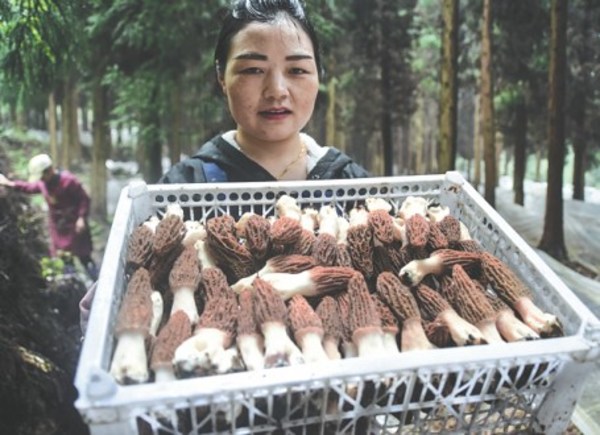

![A farmer holds a basket of edible fungus ready for selling. [photo/China Daily] A farmer holds a basket of edible fungus ready for selling. [photo/China Daily]](https://mma.prnasia.com/media2/1720152/A_farmer_holds_a_basket_edible_fungus_ready_selling__photo.jpg?p=medium600)